Tomography has made a revolutionary impact on the physical, biological and medical sciences. The mathematical foundation of tomography is to reconstruct a three-dimensional (3D) object from a set of two-dimensional (2D) projections. As the number of projections that can be measured from a sample is usually limited by the tolerable radiation dose and/or the geometric constraint on the tilt range, a main challenge in tomography is to achieve the best possible 3D reconstruction from a limited number of projections with noise. Over the years, a number of tomographic reconstruction methods have been developed including direct inversion, real-space, and Fourier-based iterative algorithms.
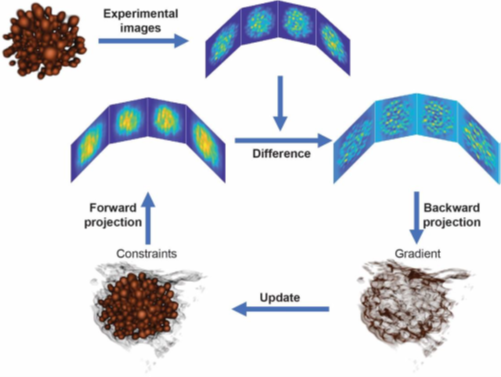
Real-space iterative reconstruction (RESIRE) algorithm is developed for accurate tomographic reconstruction. RESIRE iterates between the update of a reconstructed 3D object and the measured projections using a forward and back projection step. The forward projection step is implemented by the Fourier slice theorem or the Radon transform, and the back projection step by a linear transformation. Our numerical and experimental results demonstrate that RESIRE performs more accurate 3D reconstructions than other existing tomographic algorithms, when there are a limited number of projections with noise.
References:
1. RESIRE: real space iterative reconstruction engine for Tomography
2. RESIRE package (github.com)